
Development of tiling technology |
The development of of map service preaching technology goes from manual operation to automatic working, from standalone tiling, manual split multi-machine tiling, multi-machine parallel tiling with sharing directory to Distributed Map Tiling based on distributed storage.

Standalone machine tiling: Tiles are created in advance on a standalone machine, then the tiles are synchronized to other GIS servers in the cluster to provide map services to the outside world. This traditional tiling technology make low use of computing resources and it takes months or even years for massive data caching, which greatly affect work efficiency. What is worse, there is no obstacle recovery mechanism, the entire tiling task needs to be redone once an error occurs.

With the development of technology, the quantity of map data is growing constantly and standalone tiling cannot satisfy the needs any more. What is more, the cost for hardware resources has reduced relatively. Considering those factors, multi-machine tiling has become the first choice of many GIS applications. In a case that there is no Distributed Map Tiling tool, the multi-machine tiling method commonly used is manually splitting the tiling task into multiple child tasks according to map scales and extent, and then deploy the tasks on different machines for tiling to realize multi-machine tiling.
As to this kind of manual splitting tiling task, following disadvantages exist: manual splitting task has high requirement and it is hard to taking all factors including data accuracy, different levels of different machines, making most use of hardware resources into consideration; each machine needs manual maintenance during tiling and if single points of failure will affect the progress of the entire tiling task; the tiling task result often needs to be synchronized to other GIS servers for providing services outside while data synchronization is a task that is time consuming and prone to cause errors; if update is needed for part of the cached data, the update will be troubling and in most occasions, caching will need to be done from start again. Therefore, an automatic process for multi-machine parallel tiling is now in high demand by all industries and this technology does not rely on manual splitting of tasks and data synchronization should avoid human intervention at the same time.
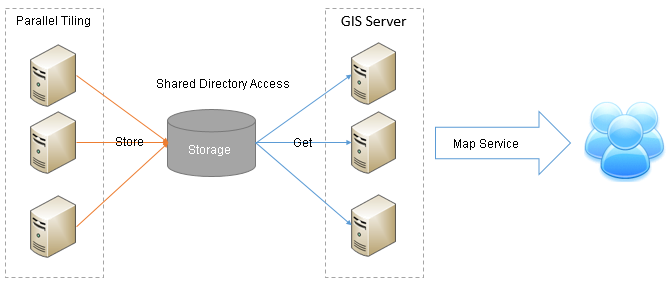
In the high demand of multi-machine tiling technology, a tiling technology based on sharing directory appears to satisfy the demand in applications. The primary features of this technology are: manual splitting is not needed for coordinating multi-machine parallel tiling and human intervention is no longer needed because map stiles are stored based on sharing directory. This kind of tiling technology can satisfy the needs to some extent. However, it cannot satisfy the needs of large scale applications. In the environment with high concurrency requirement, this type of storage mechanism based on sharing directory may encounter disk IO bottleneck problem. Once an error occurs, all work needs to be paused.
All the three methods introduced above cannot meet the challenges of high data density, high computing density, and high concurrency on massive spatial temporal data faced by the GIS map services. The bottleneck of the existing Distributed Map Tiling technology is the storage method of the map tiles. Therefore, to solve the problem, the storage mechanism of the tiling technology needs to be optimized.
Distributed Map Tiling technology introduced above use central storage server or shared directory to store map tiles. The storage server becomes the bottleneck of the system performance, and it is also the focus of system stability and security. This method cannot satisfy the requirement of large scale storage applications. However, distributed file system supports storing data in multiple distributed machines for uniform management and can solve the problem really well. The distributed file storage system employs extensible system structure and make most use of multiple storage servers to share storage burden, which not only enhances system reliability, usability, IO efficiency, but also is easy for extension.
In a period that computing hardware is upgrading in a fast speed and cloud computing is developing quickly, distributed storage technology has become mature and has been applied in multiple industries. Currently, often used distributed file systems include GFS, HDFS, Lustre, FastDFS, PVFS, GPFS, PFS, Ceph, TFS, etc. Distributed file systems have good extensibility, fault tolerance, and are transparent to internal users.
1) High usability can be realized based on redundancy recovery mechanism.
2) Hide internal storage logic and shield users and applications from differences of bottom file systems of computer modes. Uniform access interface is provided to users.
3) High extensibility. While storage capability needs to be increased, servers can be added and redesign is not needed for the storage system, which can integrate massive different storage devices in the network.
Features of distributed file system introduced above, especially advantages over shared directory (disk IO bottleneck, low reliability) enable it to become the optimal choice for map tile storage in the Distributed Tiling service.

Distributed Map Tiling technology relies on making most use of the hardware resources in the organization, implementing parallel tiling making use of multiple nodes, employing distributed file system to store tiling results, which help enhance efficiency stability, and reliability of tiling task and online services.